Tracer Injection Connection Matrix
Last updated: June 19, 2022
Overview
This page presents connection matrix visualization for the Brain/MINDS marmoset tracer injection experiments. The purpose of this matrix is to aid the viewer in finding which datasets to look at in detail by the section viewers. Each row of the matrix represents a single experiment, whereas cortical structures and regions are presented as columns. Each experiment’s injection region is indicated by a red dot. For injection positions in the flatmap, see here.
The matrix for the corticocortical projections was updated to become interactive (June 16, 2022).
Jump to
Cortical projections
Cortical projections (Lamina map)
Subcortical projections (Overview)
Subcortical projections (Brain/MINDS annotation)
Subcortical projections (MBM annotation)
For more detailed information, see technical details.
Cortical projections
⇓ ⇓ @media print only section below ⇓ ⇓
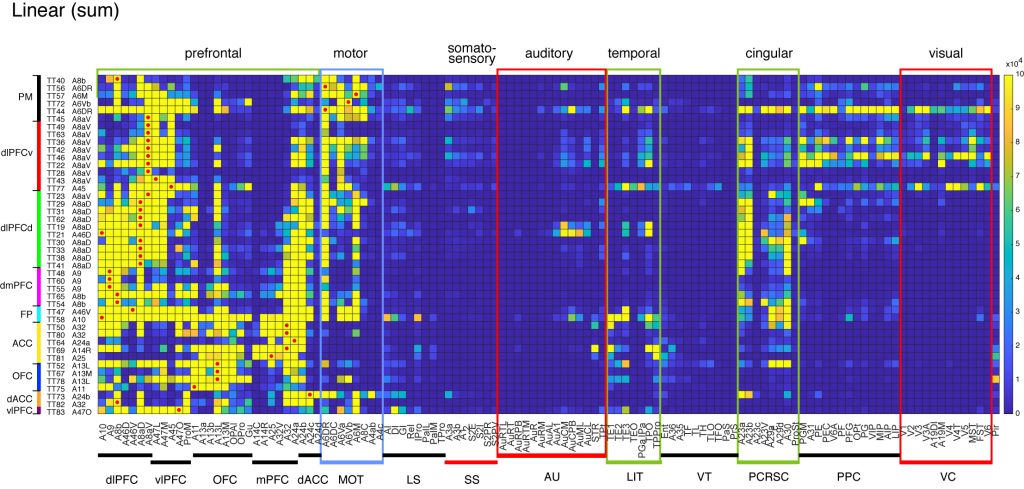
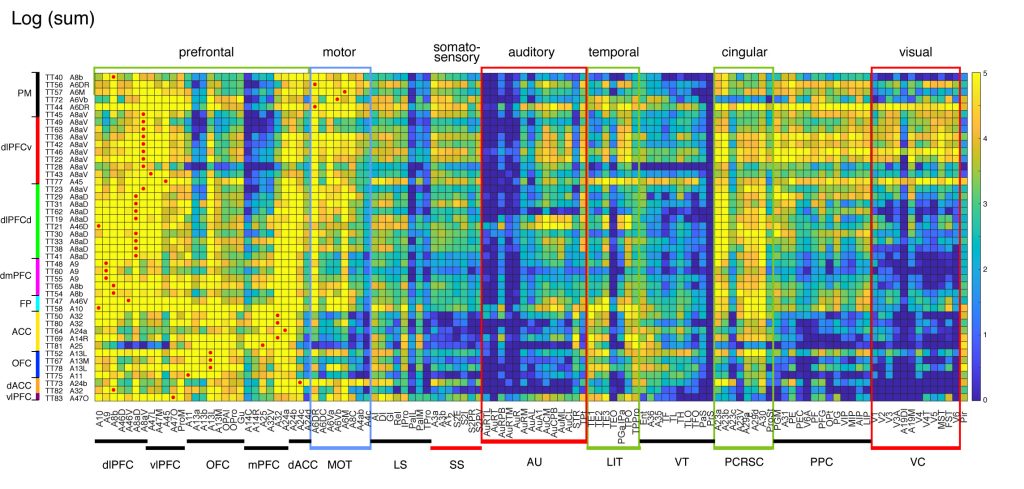
⇑⇑ @media print only section above ⇑⇑
Cortical projections (Lamina Map)
The following matrix provides lamina-specific profiles of projections to each cortical area. The tracer signals in the top, middle, and bottom layers (layer level 41-50, 21-40, and 11-20, respectively) are indicated by red, green, and blue overlaid. Note that strong signals are saturated in all colors and turn white, irrespective of true lamina preferences. Note also that the depth of injections may affect the lamina preferences in the terminal field (see technical details).
⇓ ⇓ @media print only section below ⇓ ⇓
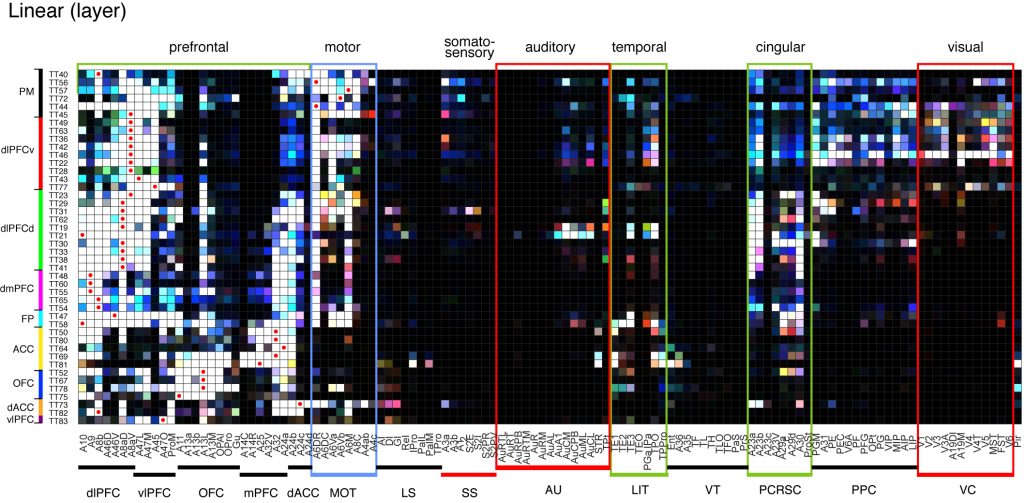
⇑⇑ @media print only section above ⇑⇑
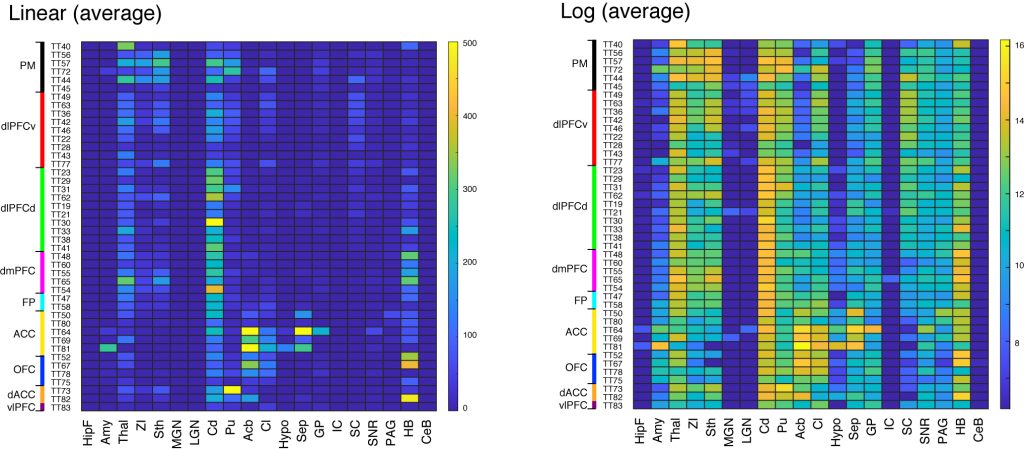
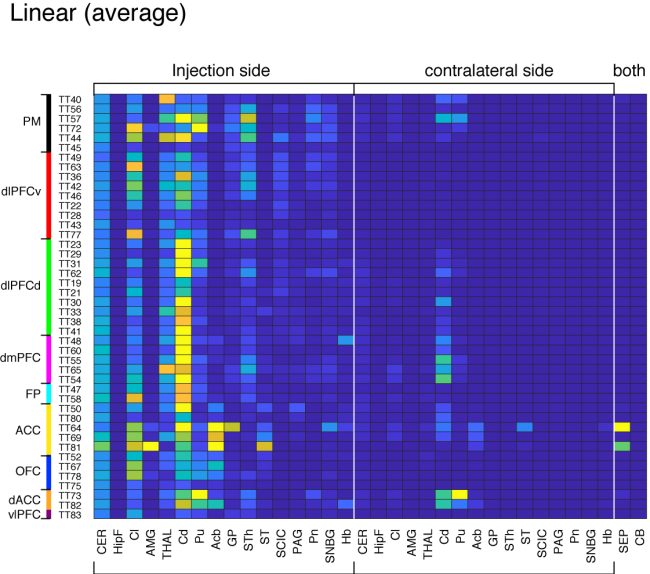
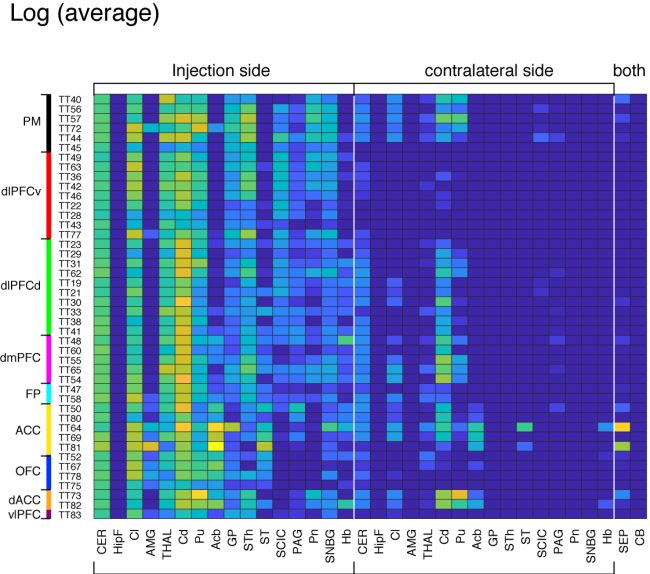
Subcortical projections (Overview; STPT annotation)
These matrices provide overview of subcortical projections from the 44 injections. The annotations are based on STPT annotation (see technical details). Here we chose the average intensity (instead of sum) for subcortical projections. The abbreviations are as follows:
CER: cerebral cortex, HipF: Hippocampal formation, Cl: Claustrum, AMG: Amygdala, THAL: thalamus, Cd: Caudate nucleus, Pu: Putamen, Acb: Accumbens nucleus, GP: Globus pallidus, STh: Subthalamic nucleus, ST: Bed nucleus of the stria terminalis, SCIC: Superiror colliculus/Inferior colliculus, PAG: Periaqueductal gray, Pn: Pontine nuclei, SNBG: substantia nigra, Hb: Habenular nucleus, SEP: Septum, CB: Cerebellum.
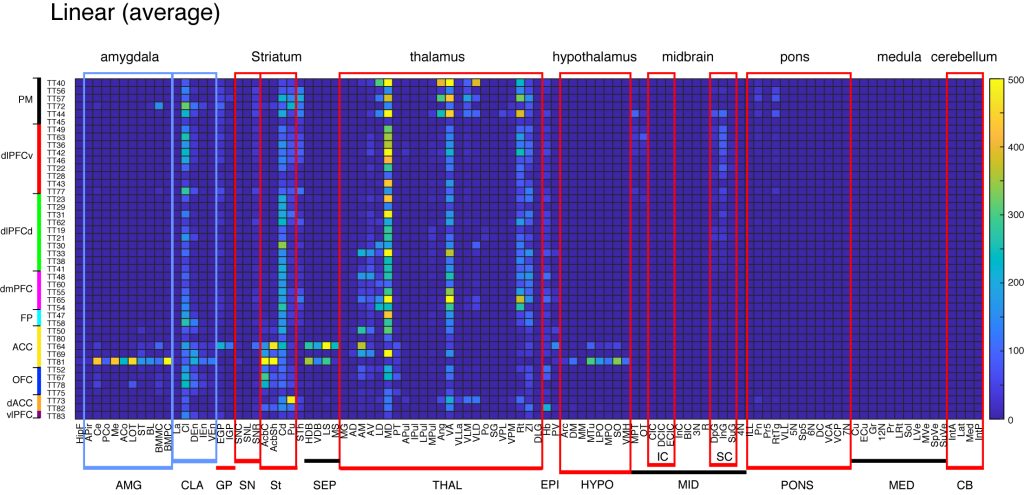
Subcortical projections (Brain/MINDS annotation)
These matrices provide a result of automatic registration to subcortical ROIs of Brain/MINDS annotation (see technical details). Here we chose the average intensity (instead of sum) for subcortical projections. Only the ipsilateral projections are shown. The abbreviations are as follows:
Hippocampal_formation_(HipF), Amygdalopiriform_transition_area_(APir), Central_amygdaloid_nucleus_(Ce), Posterior_cortical_amygdaloid_nucleus_(PCo), Medial_amygdaloid_nucleus_(Me), Anterior_cortical_amygdaloid_nucleus, Nucleus_of_the lateral_olfactry_tract_(LOT), Bed_nucleus_of_the_stria_terminalis_(ST), Basolateral_amygdaloid_nucleus_(BL), Basomedial_amygdaloid_nucleus;_magnocellular_part_(BMMC), Basomedial_amygdaloid_nucleus;_parvicellular_part_(BMPC), Lateral_amygdaloid_nucleus_(La), Claustrum_(Cl), Dorsal_nucleus_of_the_endopiriform_claustrum_(DEn), Intermediate_endopiriform_nucleus_(IEn), Ventral_nucleus_of_the_endopiriform_claustrum_(VEn), External_globus_pallidus_(EGP), Internal_globus_pallidus_(IGP), Substantia_nigra;_compact_part_(SNC), Substantia_nigra;ateral_part_(SNL), Substantia_nigra;_reticular_part_(SNR), Accumbens_nucleus;_core_(AcbC), Accumbens_nucleus;shell_(AcbSh), Caudate_nucleus_(Cd), Putamen_(Pu), Subthalamic_nucleus_(STh), Nucleus_of_the_horizontal limb_of_the_diagonal_band_(HDB), Nucleus_of_the_vertical limb_of_the_diagonal_band_(VDB), Lateral_septal_nuclei_(LS), Medial_septal_nucleus_(MS), Medial_geniculate_nucleus_(MG), Anterodorsal_thalamic_nucleus_(AD), Anteromedial_thalamic_nucleus_(AM), Anteroventral_thalamic_nucleus_(AV), Laterodorsal_thalamic_nucleus_(LD), Mediodorsal_thalamic_nucleus_(MD), Paratenial_nucleus_(PT), Anterior_pulvinar_(APul), Inferior_pulvinar_(IPul), Lateral_pulvinar_(LPul), Medial_pulvinar_(MPul), Angular_thalamic_nucleus_(Ang), Ventral_anterior_thalamic_nucleus_(VA), Ventral_lateral_thalamic_nucleus; lateral_part_(VLLa), Ventral_lateral_thalamic_nucleus;_medial_part_(VLM), Ventrolateral_thalamic_nucleus;_dorsal_part_(VLD), Posterior_thalamic_nuclear_group_(Po), Suprageniculate_thalamic_nucleus_(SG), Ventral_posterolateral_thalamic_nucleus_(VPL), Ventral_posteromedial_thalamic_nucleus_(VPM), Reticular_nucleus_(Rt), Zona_incerta_(ZI), Dorsalateral_geniculate_nucleus_(DLG), Habenular_nucleus_(Hb), Paraventricular_thalamic_nucleus_(PV), Arcuate_hypothalamic_nucleus_(Arc), Dorsomedial_hypothalamic_nucleus_(DM), Medial_mammillary_nucleus;_medial_part_(MM), Medial_tuberal_nucleus_(MTu), Lateral_preoptic_area_(LPO), Medial_preoptic_nucleus_(MPO), Supraoptic_nucleus_(SO), Ventromedial_hypothalamic_nucleus_(VMH), Medial_pretectal_area_(MPT), Nucleus_of_the_optic_tract_(OT), Central_nucleus_of_the_inferior_colliculus_(CIC), Dorsal_cortex_of_the_inferior_colliculus_(DCIC), External_cortex_of_the_inferior_colliculus_(ECIC), Interstitial_nucleus_of_Cajal_(InC), Nucleus_of_the_brachium_of_the_inferior_colliculus_(BIC), Occulomotor_nucleus_(3N), Red_nucleus_(R), Deep_gray_layer_of_the_superior_colliculus_(DpG), Intermediate_gray_layer_of_the_superior_colliculus_(InG), Superficial_gray_layer_of_the_superior_colliculcus_(SuG), Trochlear_nucleus_(4N), Intermediate_nucleus_of_the_lateral_lemniscus_(ILL), Pontine_nuclei_(Pn), Principal_sensory_trigeminal_nucleus_(Pr5), Reticulotegmental_nucleus_of_the_pons_(RtTg), Ventral_nucleus_of_the_lateral_lemniscus_(VLL), Motor_trigeminal_nucleus, Nucleus_of_the_spinal_trigeminal_tract, Abducens_nucleus, Dorsal_cochlear_nucleus, Ventral_cochlear_nucleus;_anterior_part, Ventral_cochlear_nucleus;_posterior_part, Facial_nucleus, Cuneate_nucleus, External_cuneate_nucleus, Gracile_nucleus, Hypoglossal_nucleus, Prepositus_nucleus_(Pr), Lateral_reticular_nucleus_(LRt), Solitary_nucleus_(Sol), Lateral_vestibular_nucleus_(LVe), Medial_vestibular_nucleus_(MVe), Spinal_vestizular_nucleus_(SpVe), Superior_vestibular_nucleus_(SuVe), 222 Anterior_interposed_cerebellar_nucleus_(IntA), Lateral_(dentate)_cerebellar_nucleus_(Lat), Medial_cerebellar_nucleus_(Med), Posterior_interposed_cerebellar_nucleus_(IntP).
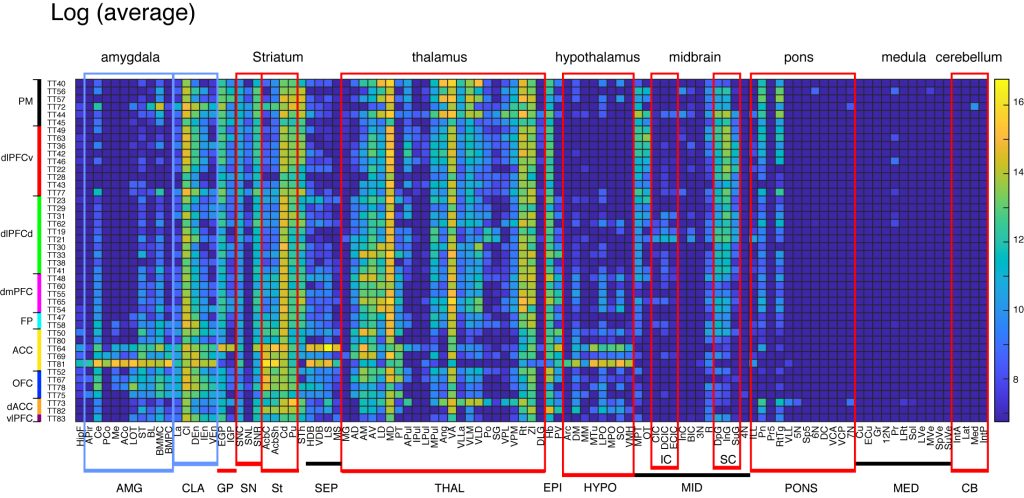
Subcortical projections (MBM annotation)
These matrices provide subcortical projections from the 44 injections, based on Marmoset Brain Mapping (MBM) annotation (see technical details). Here we chose the average intensity (instead of sum) for subcortical projections. Only the ipsilateral projections are shown. The abbreviations are as follows:
Hippocampal formation: HipF, Amygdala: Amy, Thalamus: Thal, Zona incerta: ZI, Subthalamus: Sth, Medial geniculate nucleus: MGN, Lateral geniculate nucleus: LGN, Caudate: Cd, Putamen: Pu, Acumbens: Acb, Claustrum and endopirform claustrum: Cl, Hypothalamus: Hypo, Septum: Sep, Globus pallidus: GP, Inferior colliculus : IC, Superior colliculus: SC, Substantia nigra : SNR, Periaqueductal gray : PAG, habenular nuclei: HB, Cerebellum: CeB.